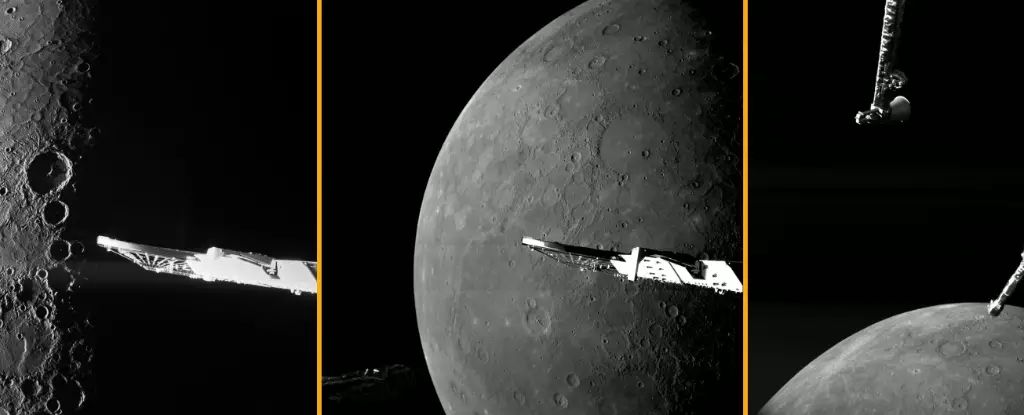
Amidst the warming glow of the Sun, Mercury stands as a peculiar celestial body, tantalizing scientists and astronomers alike with its mysteries. Recently, the European Space Agency (ESA) launched its BepiColombo mission, propelling this endeavor forward through breathtaking flybys of the innermost planet. The probe has been busy capturing intricately detailed images from just 295 kilometers away, showcasing a world of stark contrasts and extreme environments. This article explores the striking images and the scientific implications surrounding them as researchers aim to further comprehend Mercury’s enigmatic features.
One of the striking aspects of the recent images captured by BepiColombo is the revelation of countless craters adorned with the harsh illumination of continuous daylight, contrasting sharply with the shadowed terrains that hint at a mysterious ice layer nestled within. These icy enclaves are of particular interest to researchers, as they may harbor vital information about Mercury’s geological past and illuminate potential evolutionary pathways for the planet. In a statement about the mission, ESA Project Scientist Geraint Jones emphasized the urgency and excitement surrounding the findings, as each snapshot brings them closer to piecing together Mercury’s complex history.
Characterized by its small size, Mercury is barely larger than Earth’s Moon but is subject to some of the most extreme temperatures known in the solar system. At noon, temperatures can soar to a staggering 430 degrees Celsius (over 800 degrees Fahrenheit), while the frigid darkness can plunge to minus 180 degrees Celsius. This relentless battle between scorching heat and chilling cold plays a critical role in shaping the planet’s surface. Through the collected data, scientists hope to gain insights into how the planet’s atmosphere—the thinnest in the solar system—results from a harsh environment where gas is perpetually driven off and replenished through impacts and cosmic interactions.
BepiColombo’s mission is not solely about observing the surface; it is also intricately linked to understanding the forces at play beneath. Among the fascinating features captured in the images is the Nathair Facula, which bears the marks of Mercury’s most significant volcanic eruption. The central vent, with a diameter of 40 kilometers, serves as a visible reminder of geological activity that might have occurred in a not-so-distant past. Furthermore, the relatively younger Fonteyn crater—formed a mere 300 million years ago—illustrates the continuing evolution of the planet’s surface.
Researchers remain captivated by the possibilities that lie beneath the surface, including Mercury’s mysterious magnetic field and carbon reservoirs that may exist in forms believed to be diamonds. Such secrets may redefine our understanding of planetary evolution and magnetic phenomena across the solar system.
As BepiColombo nears its main operational phase, which is set to start in 2027, the anticipation among scientists is palpable. After completing its mortality-inducing gravitational assists, the mission aims to deliver expansive insights into Mercury’s attributes, encompassing its magnetism, surface features, and the sparse atmosphere. In preparation for the 2026 launch of ESA’s Mercury Planetary Orbiter and Japan’s Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter, BepiColombo will pave the way for an intricate exploration of the planet. Once deployed, these orbiters promise to enhance our understanding of Mercury further, mapping its features from altitudes and orientations that have never before been achieved.
Through the lens of BepiColombo, a vivid portrait of Mercury begins to emerge, revealing a planet of contrasts, extremes, and geological wonders. While the mission’s primary phase remains a short time away, the flybys have laid a strong foundation for future exploration. As scientists delve into the treasure trove of data and imagery, we stand at the brink of an exciting revelation about the innermost planet in our solar system—one that may shift our understanding of planetary dynamics and evolution. The journey has only just begun, and the universe of Mercury awaits.

Leave a Reply