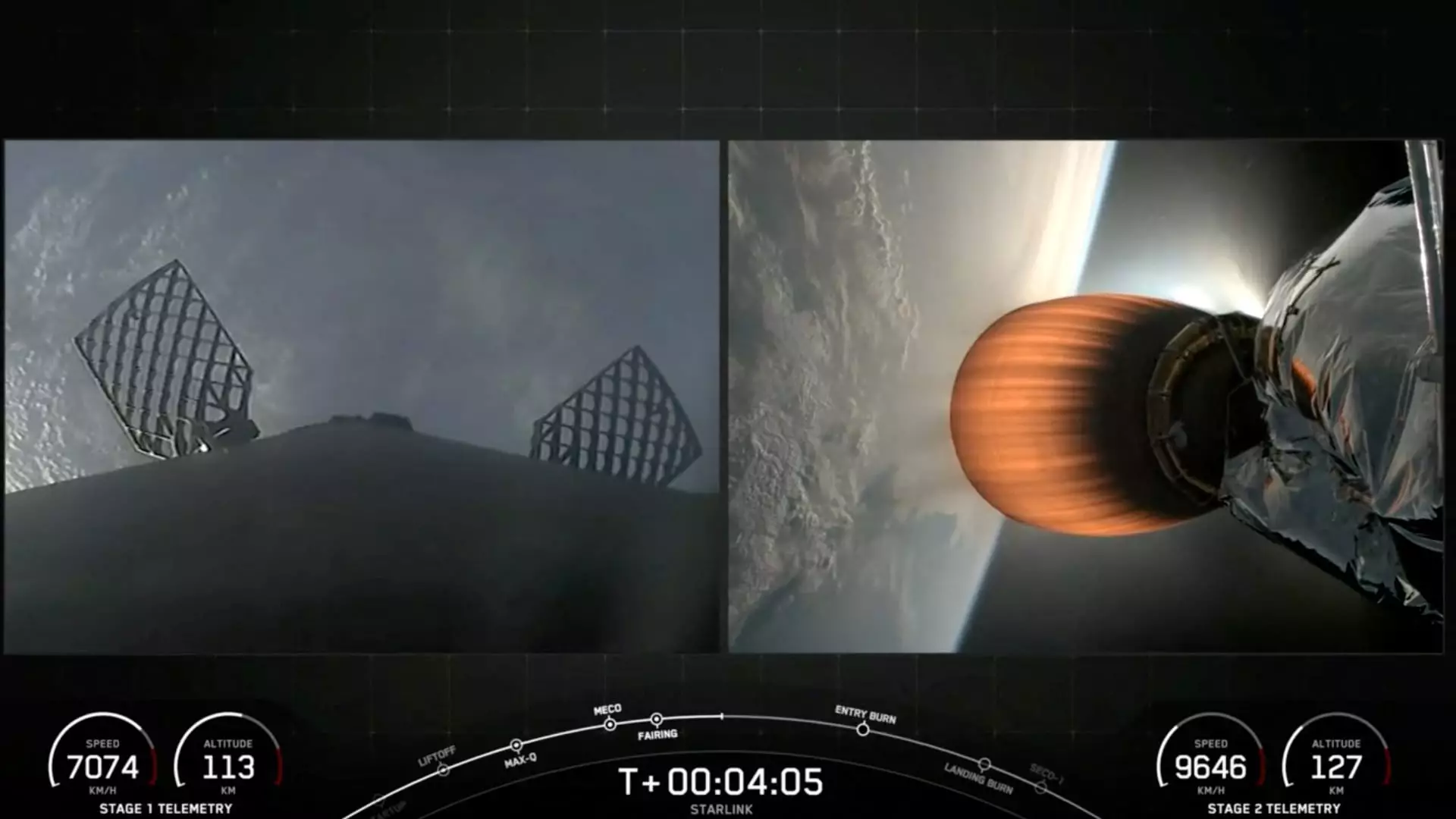
SpaceX, a renowned space exploration company founded by Elon Musk, is currently facing an unexpected setback with its Falcon 9 rocket being grounded due to an in-flight failure. This incident, which is considered rare for the company’s reliable workhorse vehicle, occurred during the “Starlink Group 9-3” mission that launched from California’s Vandenberg Space Force Base. The mission aimed to deploy 20 satellites into low Earth orbit, but encountered a critical malfunction in the upper second stage of the rocket.
The Falcon 9 rocket’s lower first stage, or booster, performed as expected by successfully returning to land. However, the upper second stage failed to reignite its engine as planned, leading to its destruction. SpaceX CEO Elon Musk acknowledged the failure, citing an “upper stage restart to raise perigee resulted in an engine RUD for reasons currently unknown.” This incident, characterized by a rapid unscheduled disassembly (RUD), was attributed to an engine failure caused by a leak of liquid oxygen in the second stage.
As a result of the in-flight failure, the Falcon 9 rocket has been grounded pending an incident investigation, requiring approval from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) before resuming operations. The FAA emphasized its role in overseeing the investigation and approval of SpaceX’s final report, including any corrective actions that need to be implemented. This regulatory involvement highlights the importance of ensuring safety and compliance in all space missions conducted by private companies like SpaceX.
The Starlink mission marked the 69th Falcon 9 launch of the year, showcasing SpaceX’s frequent launch schedule. However, the investigation into the recent failure is expected to delay upcoming launches, including two crewed missions: the private Polaris Dawn and NASA’s Crew-9. Despite successfully deploying 20 Starlink satellites, the engine failure in the second stage resulted in placing the satellites in a lower-than-intended orbit. SpaceX attempted to salvage the situation by contacting 10 of the satellites to use their onboard thrusters to adjust their orbit, but ultimately, the satellites will re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere and burn up due to the high-drag environment in the lower orbit.
Prior to this incident, Falcon 9 had maintained an impressive track record of success, with over 300 consecutive orbital launches without any in-flight failures since 2015. The rocket has played a significant role in SpaceX’s accomplishments, including the successful reuse of rocket boosters more than 280 times. However, the recent setback serves as a reminder of the inherent risks and challenges associated with space exploration, highlighting the need for rigorous safety measures and incident response protocols in place.
The unexpected grounding of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket following an in-flight failure during the Starlink mission underscores the complexities and uncertainties involved in space exploration. While setbacks are inevitable, it is crucial for companies like SpaceX to prioritize safety, regulatory compliance, and thorough investigation processes to prevent future incidents and ensure the success of their missions.

Leave a Reply